✏️ Adventure 6 — Student Activity
Use the chart to connect area to distance and velocity.
Motion: speed up, then slow down to a stop (no friction).
✳ Equations of Motion (given)
a(t)=8-2tv(t)=t(8-t)s(t)=4t²-(1/3)t³
1) How far, how fast? (Read the distance graph)
2) Area means distance (use the velocity curve)
3) Rectangle estimates (convergence idea)
Estimate total distance from 0→8 seconds by adding rectangles under v(t).
4) Velocity as area under acceleration
5) Acceleration check (0→5)
★ Calculus (optional)
s'(t)=v(t)andv'(t)=a(t)∫v(t)dtgives distance (area idea).
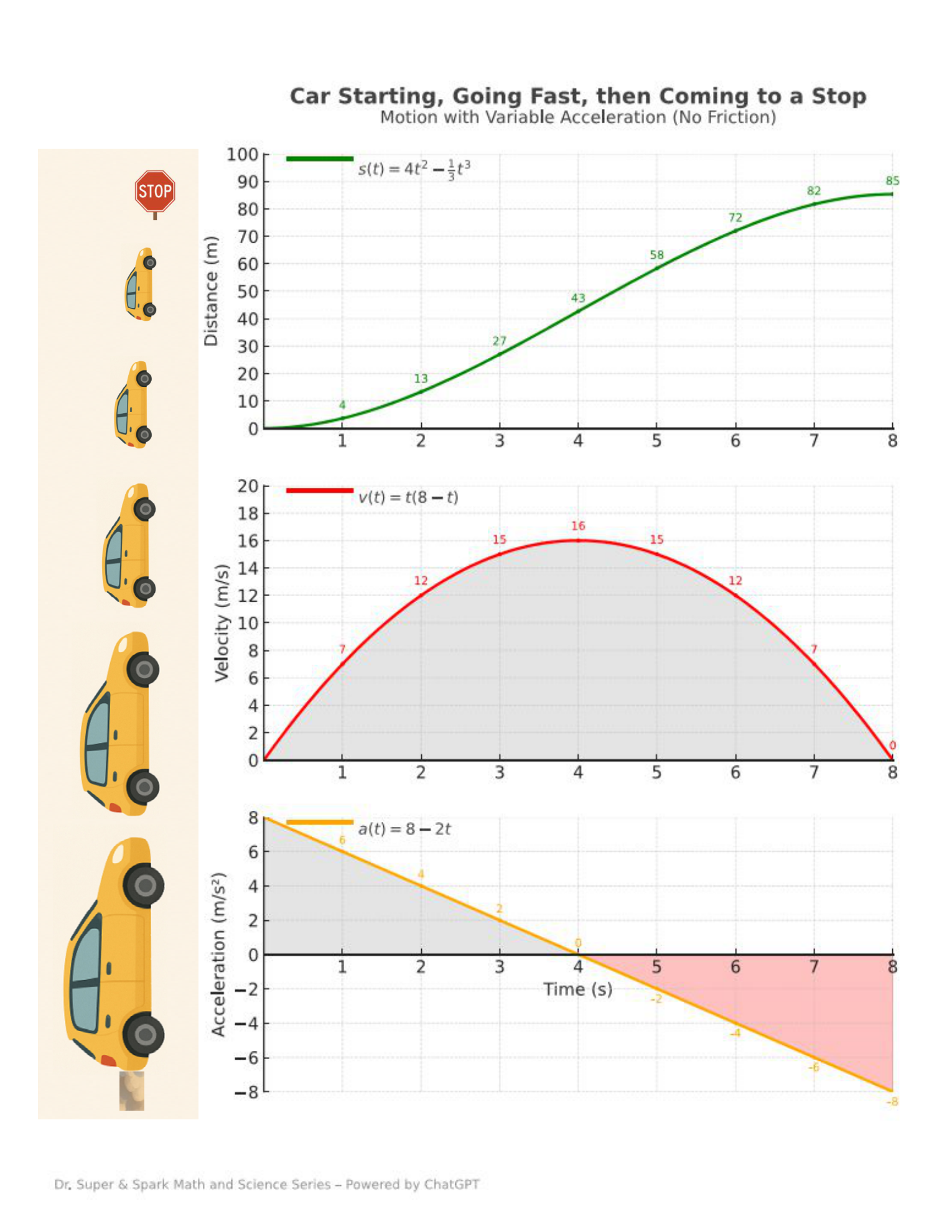
Hint: Area under v(t) is distance. Signed area under a(t) is change in velocity.
Use the labels on the curves (values at each second) to estimate.
Reference values
- Rectangle totals: Δt=1 → 84.00 m, Δt=0.5 → 85.00 m, Δt=0.25 → 85.25 m
- Exact integral (true distance): 85.33 m
- Velocity at 8 s: 0 m/s
- Change in velocity 0→5: 15 m/s