✅ Adventure 3 — Solutions
dx² and dx³ terms vanish as dx → 0.
Key idea: derivatives keep the terms proportional to dx and drop higher powers like dx², dx³.
Solution A — f(x)=x²
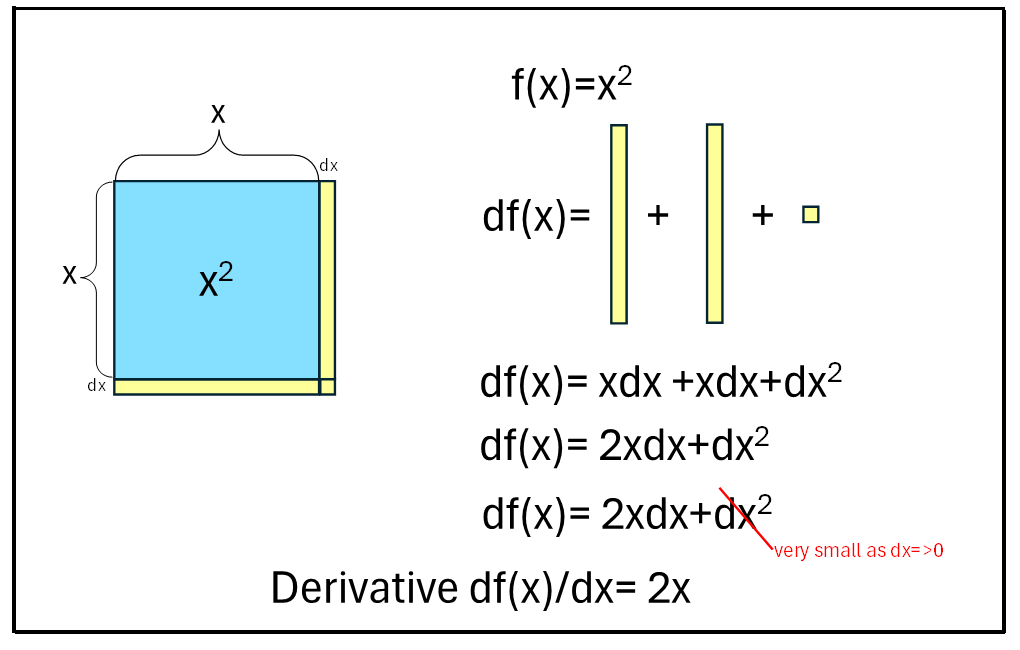
Added area pieces:
vertical strip: x·dx
horizontal strip: x·dx
corner: dx²
So df(x) = x·dx + x·dx + dx² = 2x·dx + dx².
Divide by dx:
df(x)/dx = 2x + dx.
As dx → 0, the dx term vanishes, so
d(x²)/dx = 2x.
Solution B — f(x)=x³
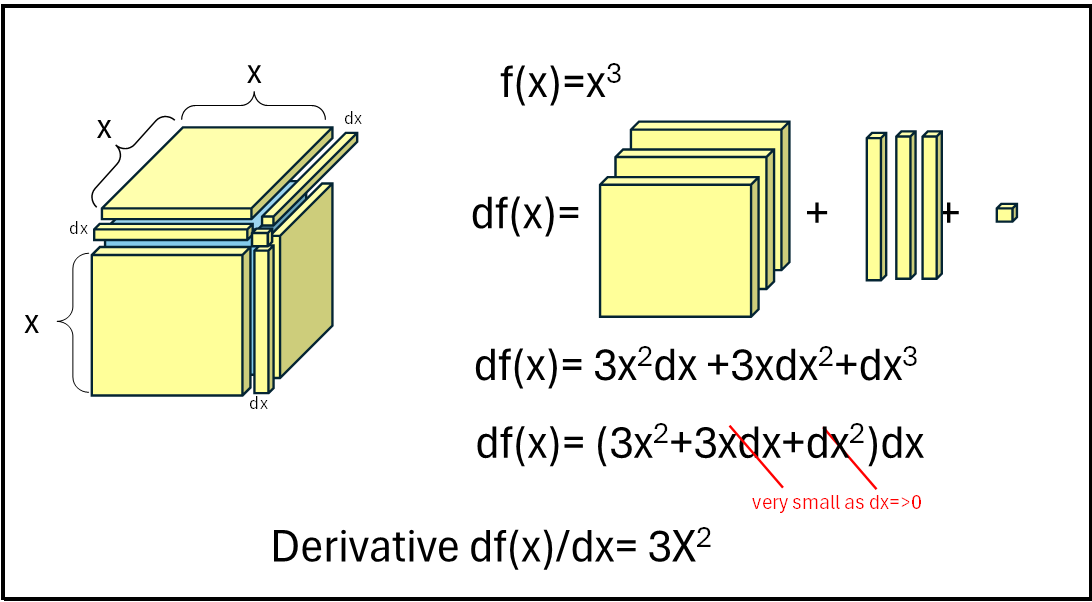
Added volume pieces:
3 face sheets: 3x²·dx
3 edge bars: 3x·dx²
1 corner cube: dx³
So df(x) = 3x²·dx + 3x·dx² + dx³.
Factor out dx:
df(x) = (3x² + 3x·dx + dx²)·dx.
Divide by dx:
df(x)/dx = 3x² + 3x·dx + dx².
As dx → 0, the last two terms vanish, so
d(x³)/dx = 3x².