🎯 Adventure 13 — Activity 1 (Solution)
Completed derivatives and tables
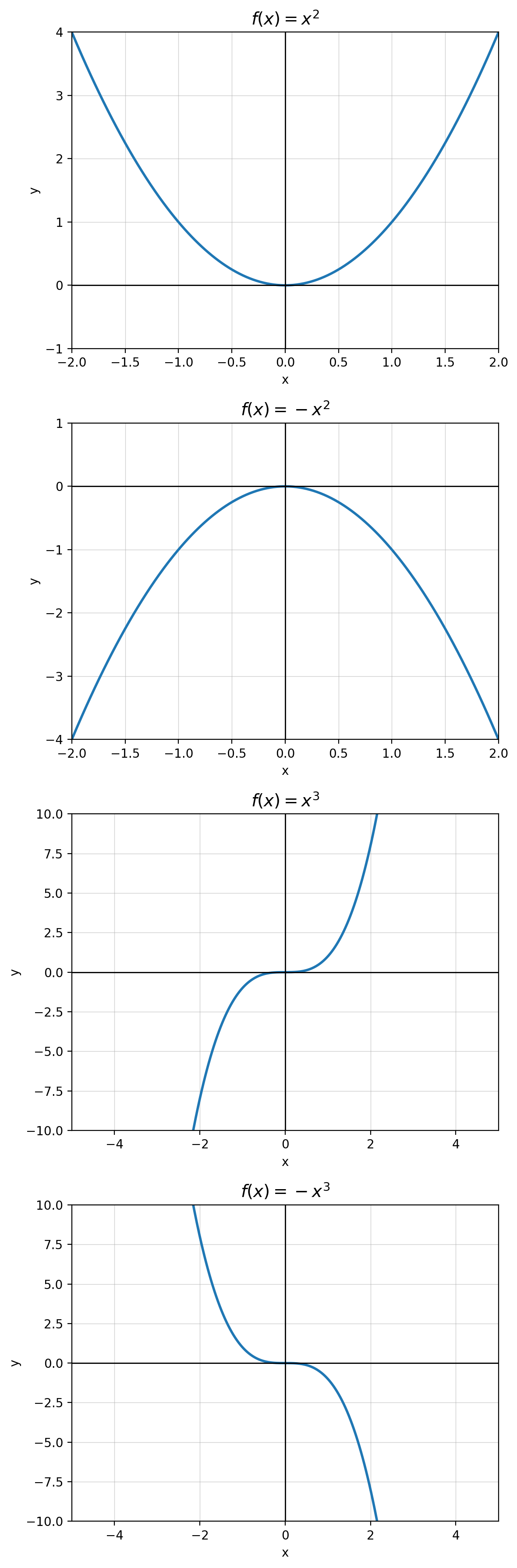
1) f(x) = x²
f′(x)= 2x f″(x)= 2
| x | f | f′ | f″ |
|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | 4 | -4 | 2 |
| -1 | 1 | -2 | 2 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
(0,0) is a minimum because f′(0)=0 and f″(0)>0.
2) f(x) = −x²
f′(x)= −2x f″(x)= −2
| x | f | f′ | f″ |
|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | -4 | 4 | -2 |
| -1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | -2 |
| 1 | -1 | -2 | -2 |
| 2 | -4 | -4 | -2 |
(0,0) is a maximum because f′(0)=0 and f″(0)<0.
3) f(x) = x³
f′(x)= 3x² f″(x)= 6x
| x | f | f′ | f″ |
|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | -8 | 12 | -12 |
| -1 | -1 | 3 | -6 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| 2 | 8 | 12 | 12 |
(0,0) is an inflection point because the concavity changes (f″ changes sign).
4) f(x) = −x³
f′(x)= −3x² f″(x)= −6x
| x | f | f′ | f″ |
|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | 8 | -12 | 12 |
| -1 | 1 | -3 | 6 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | -1 | -3 | -6 |
| 2 | -8 | -12 | -12 |
(0,0) is an inflection point because the concavity changes (f″ changes sign).